What is the Difference Between Mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine?

What is the Difference Between Mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine?
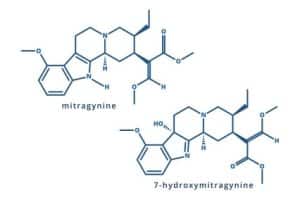
When exploring the components of the Kratom plant, commonly known by its scientific name, Mitragyna speciosa, two alkaloids stand out for their significant roles in its effects: mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine. Understanding both compounds gives us insights into how Kratom works and why it has attracted interest and controversy across various fields. In this blog, we will explore the chemical nature, biological activities, legal status, and health implications of these compounds.
Understanding Kratom’s Alkaloids
Before diving directly into the specifics of mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine, let us briefly understand what alkaloids are. Alkaloids are naturally occurring compounds mainly found in plants. They contain basic nitrogen atoms, known to have significant physiological actions on humans and other animals. Kratom contains numerous alkaloids, but mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine are the most prominent due to their potent effects.
Mitragynine: The Primary Alkaloid
Mitragynine is the most abundant alkaloid found in Kratom, constituting about 60-70% of the total alkaloid content. It is primarily responsible for the plant’s stimulating effects at low doses. Structurally, it is a tryptamine alkaloid, which suggests it has a molecular structure that somewhat resembles the neurotransmitter serotonin.
Biological Activities and Effects
Mitragynine acts predominantly on the mu-opioid receptors found in the brain, which are the same receptors that opioids like morphine bind to, but with a different spectrum of effects. At lower doses, mitragynine can elevate energy levels, enhance alertness, and increase sociability. Unlike traditional opioids, mitragynine does not induce significant euphoria or addiction when used responsibly.
Metabolism and Body Impact
Once ingested, mitragynine is processed mainly in the liver. The metabolic pathway includes the enzyme CYP3A4, which transforms it into various metabolites. Understanding this helps explain Kratom’s varying effects in different individuals, as genetic variations can alter enzyme activity.
7-hydroxymitragynine: The Secondary yet Potent Alkaloid
In contrast, 7-hydroxymitragynine accounts for only about 2% of the total alkaloid content in Kratom but is significantly more potent than mitragynine. Discovered more recently, this alkaloid has gained attention due to its potent opioid-like effects.
Biological Activities and Effects
7-hydroxymitragynine has a high affinity for the mu-opioid receptors, even more than mitragynine, which is why it’s considered more potent concerning its analgesic (pain-relieving) properties. At higher doses, it contributes predominantly to the sedative effects of Kratom, helping with pain relief and inducing relaxation and sleepiness.
Safety and Health Considerations
Given its strength and impact on the opioid receptors, 7-hydroxymitragynine’s potential for dependence and abuse is higher than mitragynine. This has been a subject of concern among health professionals and authorities, leading to regulatory scrutiny.
Comparing the Two Alkaloids
While both alkaloids interact with the mu-opioid receptors, their proportion and potency create different outcomes. Users seeking pain relief might look for Kratom strains higher in 7-hydroxymitragynine. Conversely, those interested in energy and mood enhancement might prefer strains with higher levels of mitragynine.
Legal Status and Regulatory Concerns
Globally, the legal status of Kratom and its alkaloids varies. In the United States, Kratom is not scheduled under the Controlled Substances Act, but it is banned in some states. The DEA has listed it as a “Drug and Chemical of Concern” primarily due to the presence of mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine. The concern revolves largely around inadequate scientific research to understand their long-term effects and potential health risks fully.
Usage and Health Implications
For consumers of Kratom, understanding their needs and response to the different alkaloids is crucial. Responsible usage, considering the doses and frequency, can help mitigate the risk of adverse effects. It remains essential for users to source their Kratom from reputable and trusted providers to ensure product purity and consistency.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine is fundamental for both users and researchers of Kratom. Each alkaloid contributes uniquely to the effects and risk profile of Kratom. With ongoing research and better regulatory frameworks, clearer guidelines can help maximize the benefits and minimize the risks associated with their use. The ongoing advances in analytical technologies and expanded research into these compounds will hopefully provide a clearer picture of their full potential and limitations in the future.
(Kratom Earth’s Blog is purely for educational purposes only)